Last week, the Senate Energy and Natural Resources Committee held a hearing “To Examine the Performance of the Electric Power System Under Certain Weather Conditions, Focusing on the Northeast and Mid-Atlantic Regions.” The witnesses included Andy Ott, CEO of PJM. PJM is the largest electricity grid in North America and the largest wholesale competitive electricity market in the world. In 2016, PJM’s fuel mix was 35% nuclear, 34% coal, 26% gas, and almost 5% renewables.[i] The data PJM collected during the recent Bomb Cyclone proves at least two important points. The first is that we need coal-fueled power plants. The second is that we should be cautious about relying too much on natural gas to generate electricity.
Coal Fleet
Over a four-day period (January 3-6, 2018) when the average daily temperature was 12°F, PJM relied heavily on so-called conventional sources of baseload electricity, namely, coal and nuclear. Some have implied that these fuel-secure sources of baseload electricity are outmoded, which seems to suggest that we don’t really need them anymore. However, over the four-day period, these “outmoded” electricity sources were responsible for almost two-thirds of PJM’s electricity:[ii]
- January 3 – 61% (coal + nuclear)
- January 4 – 64% (coal + nuclear)
- January 5 – 64% (coal + nuclear)
- January 6 – 64% (coal + nuclear)
Overall, coal was responsible for 37% of PJM’s electricity over the four-day period, nuclear 27%, natural gas 22%, and wind 2%.
Natural Gas
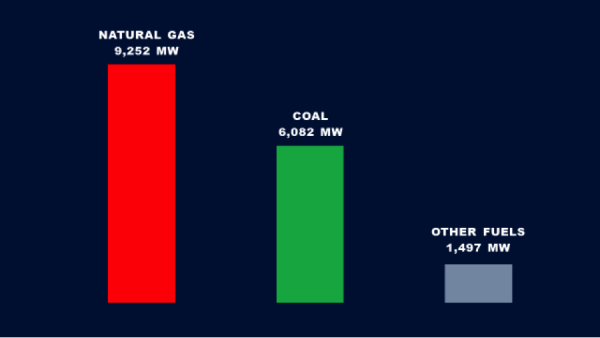
PJM provided data on forced (unplanned) outages caused solely by fuel supply problems, as well as forced outages for all causes.[iii] The first chart below is based on PJM data and shows that on January 5 when electricity demand peaked (wind chill temperature was minus 5°F that day[iv]) natural gas-fired power plants experienced 14 times more forced outages (4,395 MW) due to fuel supply issues than the PJM coal fleet (306 MW). The second chart below shows all forced outages. This chart shows that natural gas-fired power plants experienced 9,252 MW of forced outages versus 6,082 MW for the coal fleet. In short, the coal fleet outperformed the gas fleet when electricity was needed most by PJM.
Unplanned Outages on January 5 Due to Fuel Supply Issues
All Unplanned Outages on January 5
What’s my point?
During the Bomb Cyclone, PJM relied heavily on its coal fleet. Unfortunately, some 54,000 MW of coal-fueled generating capacity in PJM, MISO, ERCOT, and SPP will have retired by the end of 2020.[v] Nationwide, more than one-third of the coal fleet —111,000 MW, so far — has shut down or plans to close.[vi] According to DOE, the retirement of fuel-secure electricity sources, such as coal, is threatening the reliability and resilience of the electricity grid.[vii] There are a number of steps that should be taken to preserve the coal fleet, including properly valuing the reliability and resilience attributes of the fleet in wholesale electricity markets.
January 31, 2018
[i] Testimony of Andrew L. Ott, “Examining the Performance of the Electric Power Systems Under Certain Weather Conditions,” Senate Energy and Natural Resources Committee, January 23, 2018.
[ii] Data based on PJM Operating Committee PowerPoint presentation, “Cold Weather Summary, December 27, 2017 – January 7, 2018,” January 9, 2018.
[iii] Data based on PJM Operating Committee PowerPoint presentation, “Cold Weather Summary, December 27, 2017 – January 7, 2018,” January 25, 2018. (“January 25 PJM Presentation”) Besides unplanned outages due to fuel supply problems, PJM lists other causes as “boiler system, fuel system, electrical, emissions/environmental, pumps/fans, start failure, unit trip, and other.”
[iv] January 25 PJM presentation.
[v] ACCCE, “Retirement of U.S. Coal-Fired Electric Generating Units, Status as of January 17, 2018.” As of mid-January, some 45,000 MW of coal-fueled generating capacity in RTO/ISO regions had retired. An additional 14,500 MW are expected to retire over the period 2018-2020. Two-thirds of these future retirements have been attributed to wholesale electricity market conditions.
[vi] Ibid.
[vii] September 28, 2017 letter from DOE Secretary Perry to FERC Commissioners Chatterjee, LaFleur and Powelson regarding the need for grid resiliency rules.